
If they build it, we will go – for the long-term.
Future long-duration and deep-space exploration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond will require a way to build large-scale infrastructure, such as solar power stations, communications towers, and habitats for crew. To sustain a long-term presence in deep space, NASA needs the capability to construct and maintain these systems in place, rather than sending large pre-assembled hardware from Earth.
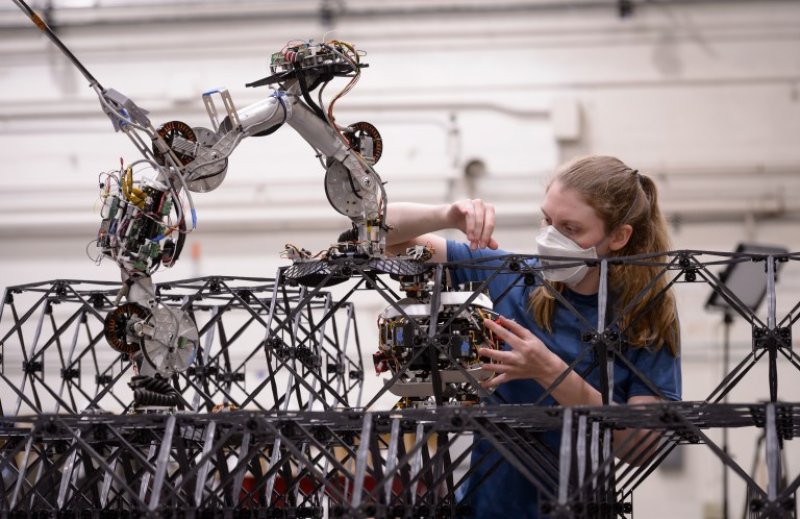
NASA’s Automated Reconfigurable Mission Adaptive Digital Assembly Systems (ARMADAS) team is developing a hardware and software system to meet that need. The system uses different types of inchworm-like robots that can assemble, repair, and reconfigure structural materials for a variety of large-scale hardware systems in space. The robots can do their jobs in orbit, on the lunar surface, or on other planets – even before humans arrive.
Researchers at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley recently performed a laboratory demonstration of the ARMADAS technology and analyzed the system’s performance. During the tests, three robots worked autonomously as a team to build a meters-scale shelter structure – roughly the size of a shed – using hundreds of building blocks. The team published their results today in Science Robotics.
“The ground assembly experiment demonstrated crucial parts of the system: the scalability and reliability of the robots, and the performance of structures they build. This type of test is key for maturing the technology for space applications,” said Christine Gregg, ARMADAS chief engineer at NASA Ames.
The high strength, stiffness, and low mass of the structural product is comparable to today’s highest-performance structures, like long bridges, aircraft wings, and space structures – such as the International Space Station’s trusses. Such performance is a giant leap for the field of robotically reconfigurable structures. Source; NASA